Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices: A Step-by-Step Guide
Patients depend on medical devices for diagnosis, treatment, and improved quality of life. So, in the healthcare industry, ensuring their safety and efficacy is crucial. Biological evaluation plays a pivotal role in determining the biological safety of medical devices. Governed by international standards, particularly the ISO 10993 series, biological evaluation involves meticulously assessing a device’s interaction with living tissues. In this guide we explore the requirements of biological evaluation, relevant regulations and biological endpoints to different devices, and the crucial role of qualified experts in the process.
ISO 10993 Standards for Biological Evaluations
The ISO 10993 standards outline vital biological endpoints for consideration during evaluation. These endpoints are essential for assessing potential risks associated with a medical device’s interaction with the human body. The findings are also pivotal for manufacturers at device development stage, supporting the refinement and revision of designs to meet necessary requirements.
The key ISO 10993 standards used for medical device biological evaluation are:
ISO 10993-1 - Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices - Evaluation and Testing within a risk management process
ISO 10993-1 serves as the cornerstone for biological evaluation of medical devices. This standard lays down the fundamental principles and methods essential for assessing the biological safety of medical devices. It provides a systematic approach that emphasizes the integration of biological evaluation into the broader risk management process applied during the development and lifecycle of medical devices. ISO 10993-1 guides manufacturers in understanding the intricacies of biological assessment, ensuring that evaluations are comprehensive, consistent, and aligned with international regulatory requirements. By adhering to the principles outlined in ISO 10993-1, manufacturers can confidently navigate the complex landscape of medical device development, ensuring the safety and well-being of patients who rely on these devices for their health and quality of life.
ISO 10993-1: Evaluation and Testing within a Risk Management Process
The cornerstone for biological evaluation of medical devices. ISO 10993-1 provides a systematic approach, which emphasises the integration of biological evaluation into the broader risk management process throughout the development and lifecycle of medical devices.
ISO 10993-2: Animal Welfare Requirements
Focused on the ethical treatment of animals during biological evaluations, this ensures humane practices and minimises potential discomfort or harm.
ISO 10993-3: Tests for Genotoxicity, Carcinogenicity, and Reproductive Toxicity
This outlines rigorous testing methods to assess genotoxic, carcinogenic, and reproductive risks associated with medical devices.
ISO 10993-4: Selection of Tests for Interactions with Blood
Critical for devices like intravascular catheters and cardiovascular implants, this provides guidelines for selecting the correct tests to evaluate interactions between medical devices and blood components.
ISO 10993-5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity
Focused on evaluating the cytotoxic potential of medical devices using in vitro methods, this standard helps manufacturers to assess the adverse effects of a device’s components on living cells.
ISO 10993-6: Tests for Local Effects After Implantatio
This standard outlines tests for assessment of the local effects of medical devices when implanted, including tissue irritation and inflammation.
ISO 10993-7: Ethylene Oxide Sterilisation Residuals
Providing guidelines for assessing the biological safety of medical devices that are sterilised using ethylene oxide gas, this standard ensures that residuals do not harm patients.
ISO 10993-9: Framework for Identification and Quantification of Potential Degradation Products
Polymeric devices, widely used in medical applications, naturally degrade, potentially releasing substances that could impact the human body. ISO 10993-9 focuses on identifying and quantifying the degradation of polymeric materials used in medical devices.
ISO 10993-10: Tests for Skin Sensitization
This standard outlines tests and methodologies for evaluating the potential irritation or sensitisation effects of a medical device on skin and mucous membranes. Adhering to the ISO 10993-10 guidelines is essential, as this not only guarantees device biocompatibility, but also enhances its overall safety profile.
ISO 10993-11: Tests for Systemic Toxicity
Critical for devices with prolonged or extensive contact with the body, such as implants, this standard outlines tests to assess systemic toxicity. This ensures that substances released from medical devices do not harm organs or tissues beyond the immediate contact area.
ISO 10993-12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials
With guidelines on preparing samples for testing, this standard emphasises the importance of using appropriate reference materials. This ensures that test results are valid and consistent across laboratories, supporting accurate comparisons of results. It also highlights the importance of using reference materials to calibrate instruments and validate testing methods, ensuring precision in biological evaluations.
ISO 10993-13: Identification and Quantification of Degradation Products from Polymeric Medical Devices
As polymeric devices naturally degrade, identifying and quantifying degradation products is crucial to understanding potential impact on human health. ISO 10993-13 focuses on identifying and quantifying degradation products from polymeric materials over time.
ISO 10993-14: Identification and Quantification of Degradation Products from Ceramics
Given the long-term application of ceramic devices, understanding the nature and quantity of degradation products is vital to guarantee safety and effectiveness across their lifecycle. This standard outlines methodologies to evaluate potential degradation products from ceramic medical devices.
ISO 10993-15: Identification and Quantification of Degradation Products from Metals and Alloys
Metals and alloys are often used in medical devices for mechanical strength and resilience.
However, over time, these materials may degrade, potentially releasing harmful substances into the body. This standard provides procedures to identify and quantify degradation products from metals and alloys used in medical devices.
ISO 10993-16: Toxicokinetic Study Design for Degradation Products and Leachables
Crucial in medical device evaluation, this standard outlines guidelines for designing toxicokinetic studies to understand how degradation products and leachables are absorbed, distributed, metabolised, and excreted by the human body.
ISO 10993-17: Toxicological Risk Assessment of Medical Device Constituents
By conducting rigorous toxicological assessments, manufacturers can identify and mitigate hazards associated with the components used in their devices. This standard provides guidelines for systematically evaluating potential toxicological risks in the constituents of medical devices.
ISO 10993-18: Chemical Characterization of Medical Device Materials
Understanding the exact chemical makeup of materials used in medical devices is crucial as they directly influence biocompatibility and potential risk to patients. ISO 10993-18 provides guidelines for evaluating the chemical composition of materials used in medical devices within a risk management process.
ISO 10993-19: Physico-Chemical, Morphological, and Topographical Characterization of Materials
By learning about medical device materials at a fundamental level, manufacturers can gain essential insights into how they interact with biological systems, ensuring safety and efficacy.
ISO/TS 10993-19 provides guidelines for understanding the physical and chemical properties of these materials, as well as their structural characteristics.
ISO 10993-20: Principles and Methods for Immunotoxicology Testing of Medical Devices
Immunotoxicology testing assesses how medical devices might trigger adverse reactions in the immune system. ISO/TS 10993-20 outlines guidelines for evaluating immunological responses from medical devices. This helps manufacturers understand a device’s potential to induce allergic reactions, hypersensitivity, or other immune-related complications.
ISO 10993-22: Guidance on Nanomaterials
This standard plays a pivotal role, fostering medical innovation while protecting patient health. Providing comprehensive advice on experimental techniques, risk assessment, and considerations tailored to nanomaterials, it ensures a thorough understanding of their effects on living tissues.
ISO 10993-23: Tests for Irritation
Covering various methods, including in vitro and in vivo assessments, this standard provides a comprehensive approach towards revealing a device’s potential to cause irritation or inflammation of living tissues.
ISO 10993-33: Guidance on Tests to Evaluate Genotoxicity
Genotoxicity testing is crucial as it examines whether a device’s components can induce mutations or damage genetic material in cells, which may lead to health conditions, including cancer. To address these risks, ISO 10993-33 provides guidance on tests evaluating the genotoxicity of medical devices and assessing potential genetic damage.
Selecting the Right Biological Endpoints
Types of Medical Devices
There are three primary types of medical devices when it comes to biological evaluation:
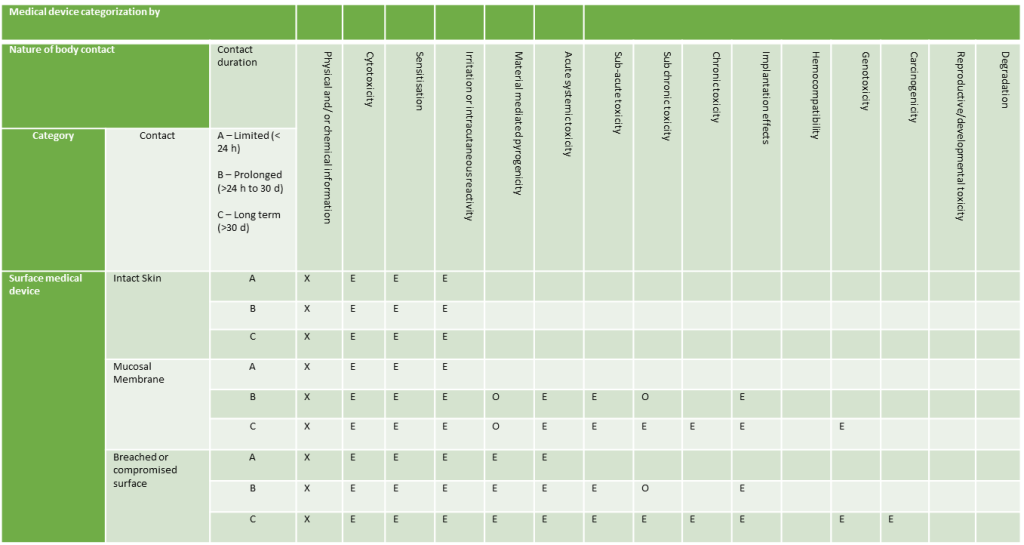
- Surface Devices: Devices in contact with skin, mucosal membranes, or breached surfaces.
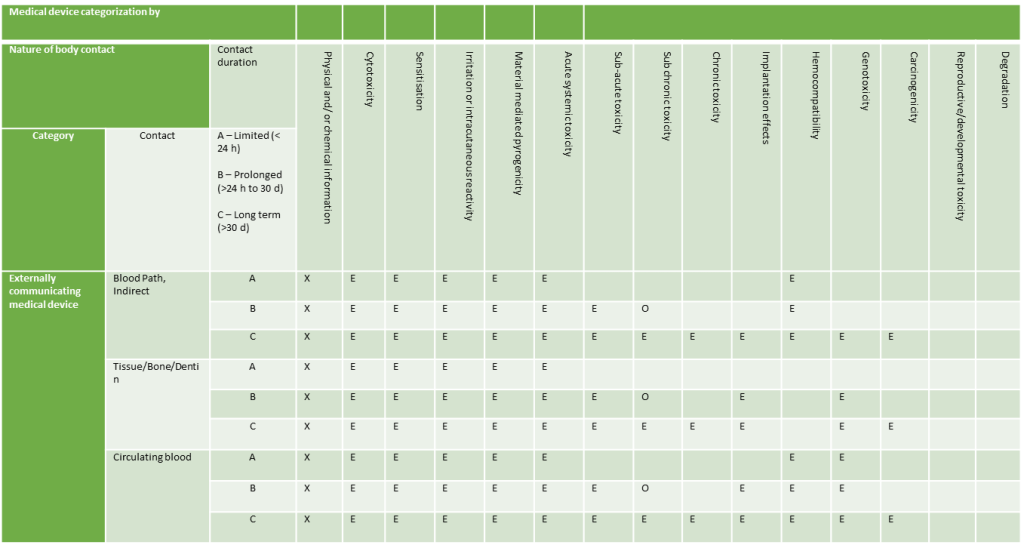
- Externally Communicating Devices: Devices in contact with blood, tissue/bone/dentin, or circulating blood.
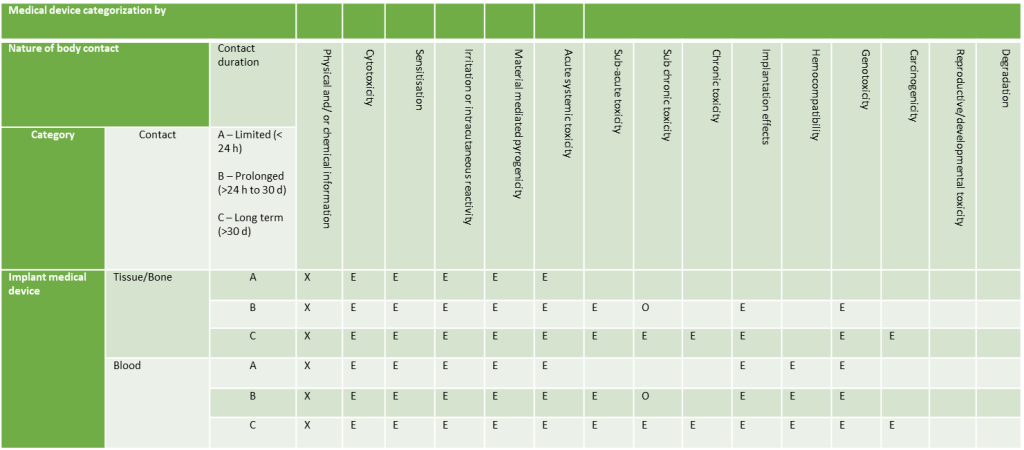
- Implant Devices: Devices in contact with tissue/bone or blood.
Duration of Contact
The duration of contact time also determine which biological endpoints are relevant. This also applies to medical devices with a cumulative contact time. These devices are applied for a few minutes or hours and not applied until later. Based on this cumulative contact time over the user’s lifetime, the same user needs should be considered.
Contact times are categorised as follows:
- Less than 24 hours
- Between 24 hours and 30 days
- Over 30 days
Applicable Biological Endpoints
Surface Devices
Externally Communicating Devices
Implantable Devices
Conducting Biological Evaluations
Carrying out biological evaluations requires rigorous and comprehensive reporting. To comply with regulations, you will need a Biological Evaluation Plan (BEP) and Biological Evaluation Report (BER) prepared by a qualified professional.
Biological Evaluation Plan (BEP)
To assess the relevant biological endpoints associated with their products, manufacturers must create a comprehensive Biological Evaluation Plan (BEP). Serving as a vital document, the BEP outlines and identifies the biological endpoints relevant to the medical device under evaluation, relying on rigorous testing or scientific literature. The BEP is critical for thorough and accurate evaluations, and should align with relevant standards outlined above and the manufacturer’s risk management plan.
Biological Evaluation Report (BER)
Following testing and the collection of scientific evidence, a comprehensive Biological Evaluation Report (BER) must be prepared.
Essential in the medical device industry, the BER evidences that all relevant biological endpoints have been assessed, ensuring that the device is biologically safe.
The BER holds significant importance as a validation document, showing compliance with Medical Device Regulations. It is also a vital component of the verification and validation process and must be prepared by a qualified professional, such as a toxicologist.
Need assistance with BEPs and BERs? Speak to an expert from Patient Guard BE Support.




