Medical Device Quality Failures
Over the last century medical devices have revolutionised healthcare. Most medical devices work as intended and are beneficial to the patient. However, when they are badly manufactured or designed they can go wrong on a spectacular level. Here we take a look at the top 3 medical device quality failures over the last few decades.
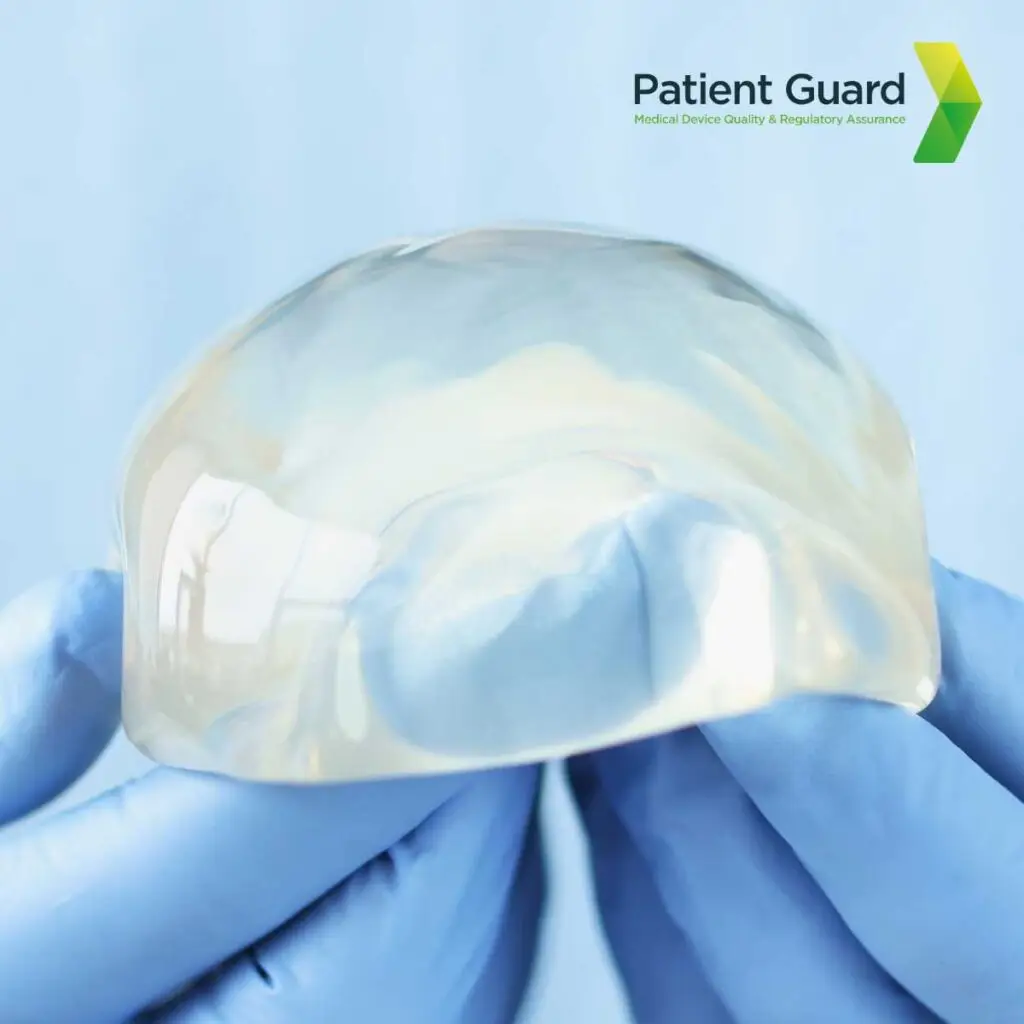
1. PIP Breast Implant Scandal
The PIP breast implant scandal exposed a major failure in regulatory oversight and corporate ethics within the medical device industry. French company Poly Implant Prothèse (PIP) was found to have used industrial-grade silicone, not approved for medical use, in its breast implants. This cost-cutting measure resulted in implants with a higher likelihood of rupturing and causing health complications, including inflammation and potential exposure to harmful substances. The scandal highlighted significant gaps in the EU’s medical device regulatory framework at the time, particularly in post-market surveillance and conformity assessment processes. It prompted widespread reforms, including the introduction of the stricter EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), to ensure better patient safety and manufacturer accountability.
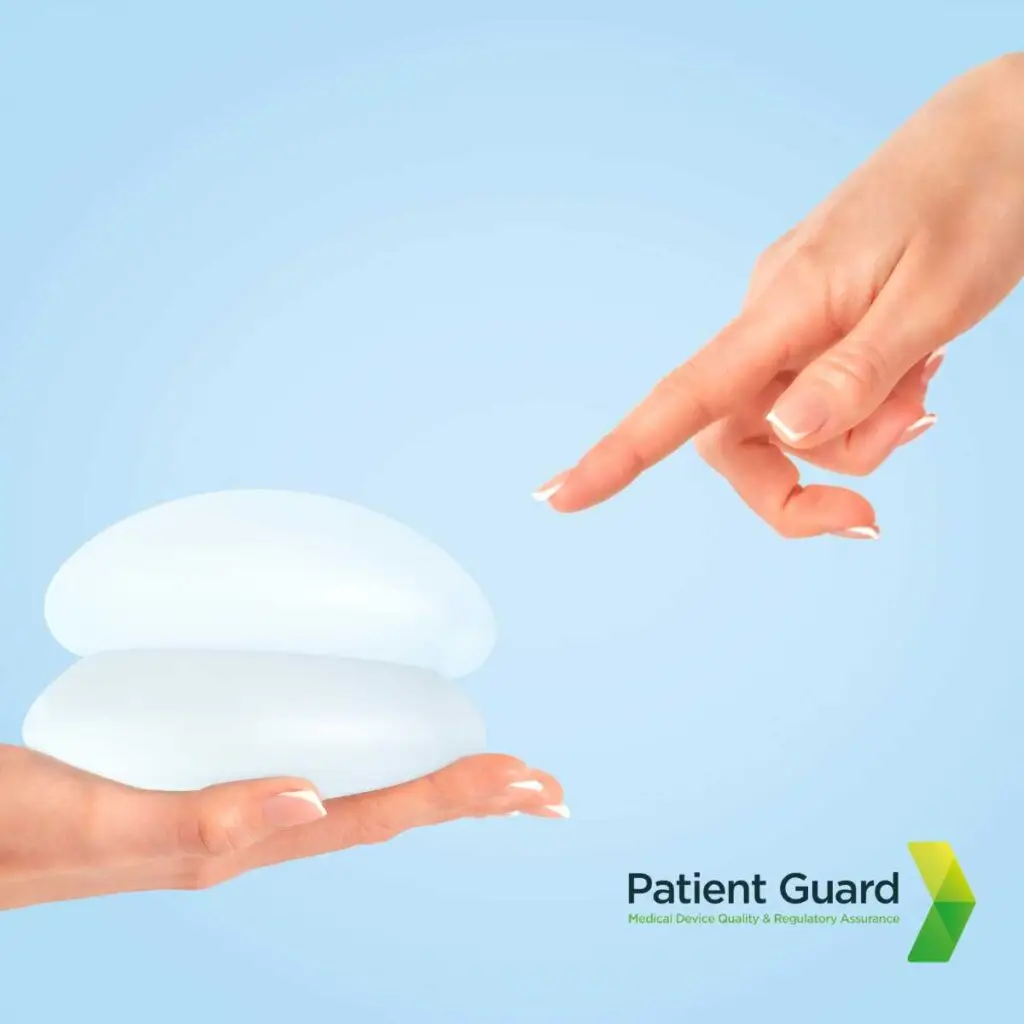

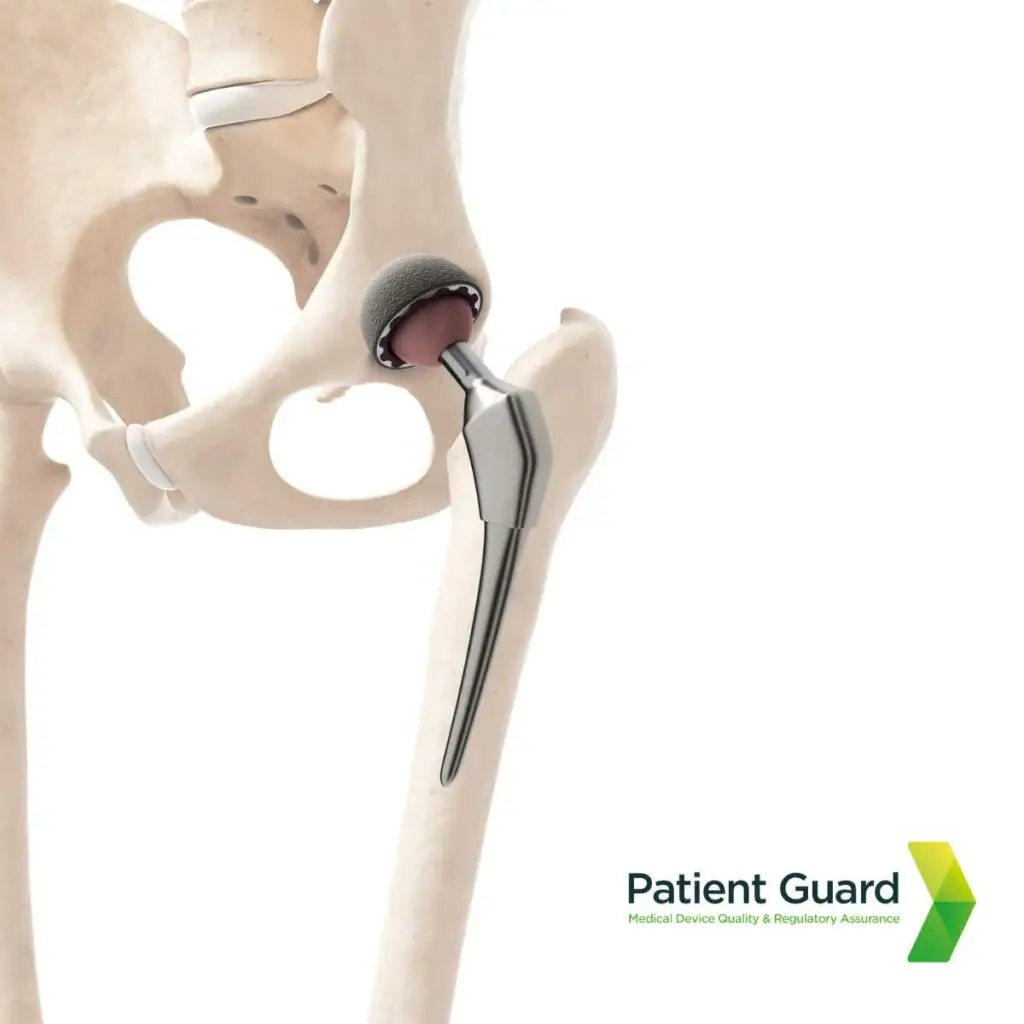
2. Metal on Metal Hip Implant Scandal
The metal-on-metal hip implant scandal revealed critical flaws in both product design and regulatory oversight. These implants, marketed as durable and innovative solutions for joint replacement, were later found to release toxic metal ions into patients’ bodies due to wear and tear between the metal components. This caused severe health issues, including tissue damage, inflammation, and systemic metal poisoning. Manufacturers failed to adequately test these devices’ long-term safety, while regulatory systems at the time lacked rigorous pre-market and post-market surveillance. The scandal underscored the need for stricter safety assessments and monitoring, prompting reforms such as those introduced under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) to improve patient protection.
3.Vaginal Mesh Scandal
The vaginal mesh scandal exposed serious shortcomings in medical device design, testing, and regulatory approval processes. Vaginal mesh implants, used to treat pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence, were later found to cause severe complications in many patients, including chronic pain, organ perforation, and infection. The materials and designs were often inadequately tested for long-term safety and efficacy, and some devices were approved with minimal clinical evidence. Additionally, insufficient post-market surveillance allowed these issues to persist unchecked for years. The scandal led to global recalls, lawsuits, and stricter regulatory requirements, including the EU MDR’s emphasis on clinical evidence and ongoing safety monitoring to better protect patient health.
How have these scandals changed medical device regulation?
The PIP breast implant, metal-on-metal hip, and vaginal mesh scandals significantly reshaped global medical device regulations, highlighting critical weaknesses in pre-market evaluation, post-market surveillance, and transparency. These incidents exposed gaps in clinical testing, traceability, and manufacturer accountability, prompting regulators to adopt stricter measures to protect patient safety.
In the EU, these scandals were a driving force behind the introduction of the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), replacing the older directives. These new regulations demand stronger clinical evidence, robust post-market surveillance systems, and unique device identification (UDI) for improved traceability. The MDR also imposes stricter oversight of Notified Bodies, ensuring more rigorous conformity assessments.
Globally, similar changes have emerged, including enhanced requirements for clinical trials, improved adverse event reporting, and stricter enforcement of manufacturer responsibilities. These reforms aim to restore trust in the medical device industry and minimize the risk of future scandals, prioritizing patient safety above all else.
Summary
The PIP breast implant, metal-on-metal hip, and vaginal mesh scandals exposed critical medical device quality failures that jeopardized patient safety and trust. These incidents revealed significant deficiencies in pre-market testing, clinical evaluation, and post-market surveillance, allowing unsafe devices to remain on the market for years. As a result, regulatory frameworks worldwide underwent transformative reforms to address these issues. The EU introduced the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR), prioritizing stricter clinical evidence requirements, enhanced surveillance systems, and robust traceability measures. Globally, similar measures were implemented to mitigate risks and hold manufacturers accountable for medical device quality failures. These changes aim to ensure safer devices, prevent future scandals, and restore confidence in the industry by addressing past medical device quality failures comprehensively.
FAQs
Patient Guard specializes in creating and implementing robust Quality Management Systems (QMS) that align with global standards like ISO 13485. We assist with:
- Developing comprehensive policies and procedures.
- Conducting gap analyses to identify and address deficiencies.
- Providing training for staff on regulatory compliance and best practices.
Key insight: A well-implemented QMS ensures consistent product quality and smooth regulatory audits.
Patient Guard ensures manufacturers comply with regulations such as the EU MDR, IVDR, and FDA Quality System Regulation (QSR) by:
- Preparing technical documentation for regulatory submissions.
- Assisting with device classification and risk management aligned with ISO 14971.
- Offering ongoing support for post-market surveillance and vigilance reporting.
Pro tip: Staying compliant reduces the risk of fines, recalls, and delays in market access.
Patient Guard helps manufacturers avoid quality pitfalls by:
- Establishing effective supplier evaluation and monitoring systems.
- Developing quality control processes for inspections and testing.
- Ensuring traceability from raw materials to finished devices.
Key takeaway: Proactive quality management minimizes the chances of defects and non-conformities.
Yes! Patient Guard provides full support for regulatory inspections by:
- Conducting pre-audit readiness assessments.
- Addressing potential non-conformities before audits.
- Offering on-site or remote support during inspections.
Why it matters: Proper preparation helps manufacturers demonstrate compliance and avoid penalties or certification delays.
Patient Guard offers a proven track record of helping manufacturers enhance quality systems and avoid costly pitfalls. Our services include:
- Tailored solutions for ISO 13485 compliance and regulatory readiness.
- Expert support for technical documentation, risk management, and post-market activities.
- Training and guidance to build long-term quality and compliance capabilities.
Why choose Patient Guard: With experience supporting over 500 clients, we ensure your processes are optimized to meet regulatory requirements and deliver high-quality products.